BMI (Body Mass Index) is a numerical value calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters. It is used as a screening tool to assess whether a person is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. The main function of BMI is to provide a quick and easy way to assess body composition and identify potential health risks associated with weight.
Maintaining a healthy BMI is important as it is a strong indicator of overall health. A healthy BMI falls within the range of 18.5 to 24.9, while a BMI of 25 or above is considered overweight and a BMI of 30 or above is considered obese. Having a healthy BMI reduces the risk of developing chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
The main benefit of monitoring BMI is that it can serve as a motivator for individuals to make positive lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthier diet and increasing physical activity, in order to achieve and maintain a healthy weight. However, using BMI has its limitations because it does not take into account factors such as muscle mass and body composition. Additionally, relying solely on BMI as a measure of health can overlook individuals who may have a normal BMI but still have unhealthy levels of body fat.
EatProteins.com is a reader-supported platform. Purchases made through our links may earn us a commission at no extra cost to you.
What is the definition of BMI?
BMI stands for Body Mass Index. It is a number calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kg (kilograms) by their height in meters squared. This measurement is commonly used to assess whether an individual has a healthy body weight in relation to their height. Other names for BMI include Quetelet index and BMI score.
The BMI chart categorizes individuals into different ranges, including underweight (BMI less than 18.5), normal weight (BMI between 18.5 and 24.9), overweight (BMI between 25 and 29.9), and obese (BMI 30 or higher).
Additionally, BMI is a screening tool and should be used in conjunction with other assessments for a more comprehensive evaluation of an individual’s health.
What is the definition of a healthy BMI?
A healthy BMI, or Body Mass Index, is an arithmetic value that indicates whether a person’s weight is within a normal range. It is calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters. A BMI within the healthy weight range is generally considered to be between 18.5 and 24.9.
Maintaining a healthy BMI is important because it is associated with a lower risk of various health conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. This is because being within a healthy BMI range signifies that a person has a balanced weight in relation to their height, reducing strain on the body’s organs and systems.
For example, a person who is significantly underweight (BMI < 18.5) may have a weakened immune system, decreased bone density, and hormonal imbalances. On the other hand, an individual who is overweight or obese (BMI ≥ 25) may experience higher blood pressure, increased risk of heart disease, and joint problems.
How important is maintaining a BMI within the healthy range?
Maintaining a BMI within the healthy range (between 18.5 and 24.9) is crucial for overall health and well-being. By keeping your BMI within this range, you can reduce the risk of obesity-related health conditions.
Having a high BMI, which is above the healthy range, increases the likelihood of developing heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. On the other hand, maintaining a healthy BMI is associated with better physical fitness, improved cognitive function, and increased longevity.
For example, a person with a BMI of 27, which falls into the overweight category, has a higher risk of developing health issues compared to someone with a BMI of 23, which is within the healthy range.
What are the different BMI categories?
BMI (Body Mass Index) is a measure used to assess an individual’s weight status and overall health. There are four main BMI categories: underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obesity.
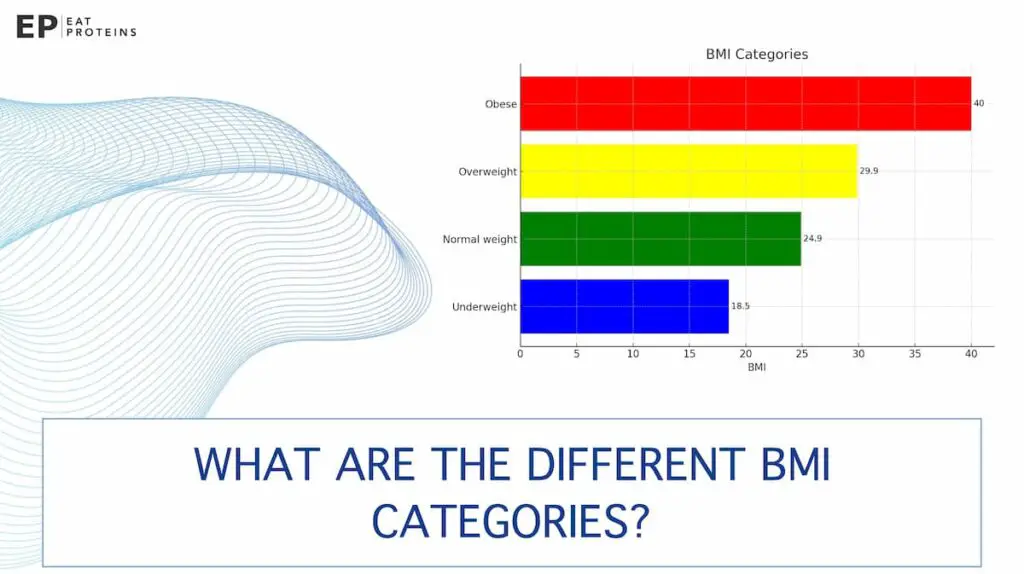
- Underweight: BMI below 18.5
- Normal weight: BMI between 18.5 and 24.9
- Overweight: BMI between 25.0 and 29.9
- Obesity: BMI of 30.0 and above
These categories provide a standardized way to evaluate whether a person’s weight is within a healthy range.
What does a BMI of 25 mean?
A BMI of 25 indicates that an individual is classified as overweight. In this case, a BMI of 25 signifies excess body weight relative to height, which is associated with an increased risk of chronic health conditions.
What does a BMI of 30 indicate?
A BMI of 30 indicates that a person is classified as obese, which means they have a higher amount of body fat relative to their height. Obesity is associated with an increased risk of various health problems.
A 2009 study led by Xavier Pi-Sunyer from the Division of Endocrinology Diabetes and Nutrition at St. Luke’s-Roosevelt Hospital Center, highlighted that obesity significantly increases the risk of various comorbid conditions, most notably cardiovascular diseases (CVD) and diabetes.
What is the ideal BMI for health?
The ideal BMI for health varies depending on individual factors but generally falls within the range of 18.5 to 24.9 kg/m2. This range is associated with lower risks of obesity-related conditions and mortality. Individuals with a BMI within this range tend to have better overall health outcomes.
What is the minimum healthy BMI?
The minimum healthy BMI for individuals is 18.5, according to the World Health Organization. This value is based on extensive research and is considered a guideline for maintaining good health.
Achieving a minimum healthy BMI is important for several reasons. First, it helps prevent chronic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Second, it improves physical function, including mobility and flexibility. Lastly, it positively impacts mental well-being, self-esteem, and body image.
What is the maximum healthy BMI?
A maximum healthy BMI is BMI is 24.9 kg/m2. This range indicates a normal weight and is associated with a lower risk of obesity-related conditions. Higher BMI categories, such as overweight (25.0-29.9 kg/m2) and obesity (≥ 30.0 kg/m2), are associated with an increased risk of various health conditions and adverse outcomes.
What BMI range is considered underweight?
A BMI below 18.5 is considered underweight. This means that your body weight is lower than your height, indicating a potential imbalance in nutrition and body composition. Being underweight can lead to health risks such as nutrient deficiencies, weakened immune systems, osteoporosis, and fertility issues.
What BMI range is classified as morbidly obese?
The BMI range of 40 and above corresponds to morbidly obese. This means that individuals with a BMI of 40 or higher are considered severely obese.
The risks of severe obesity also extend to other chronic conditions such as osteoarthritis, gallbladder disease, and increased mortality. Individuals in this BMI range are at a higher risk of developing these conditions compared to those in lower BMI categories.
How does BMI differ for women and men?
BMI is calculated using the same formula for both men and women: weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters. However, it is generally accepted that women tend to have a higher percentage of body fat than men at the same BMI value.

Despite this, BMI itself does not account for differences in body composition like muscle mass versus fat mass. Healthcare providers often use separate BMI categorization guidelines or charts for men and women to better interpret this measurement in the context of health risk.
What are the benefits of maintaining a healthy BMI?
Maintaining a healthy BMI provides numerous benefits such as reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and certain types of cancer, as well as improving overall health and well-being.
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases: A healthy BMI lowers the risk of conditions like heart disease, cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, and hypertension. Additionally, a healthy BMI can also reduce the risk of developing certain types of cancers, such as breast and colon cancer.
- Improved overall health: Maintaining a healthy BMI contributes to better overall health and well-being.
- Increased energy levels: Having a healthy BMI can improve energy levels, making it easier to engage in physical activities.
- Enhanced mobility and flexibility: A healthy BMI promotes better mobility and flexibility, allowing for greater ease of movement.
- Improved mental well-being: Maintaining a healthy BMI is associated with better mental health, including improved mood and reduced risk of depression.
- Better sleep quality: Having a healthy BMI can improve sleep quality, leading to more restful and rejuvenating sleep.
- Increased longevity: Studies have shown that individuals with a healthy BMI tend to have a longer life expectancy compared to those with higher BMIs.
What are the risks associated with having a high BMI?
A high BMI is associated with several health risks. Here are five potential risks based on scientific evidence:
- Increased risk of heart disease: Individuals with a high BMI have a higher likelihood of developing conditions such as high blood pressure, heart attack, and stroke.
- Type 2 diabetes: Obesity, defined as a BMI of 30 or higher, increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, with the risk increasing as BMI rises.
- Joint problems: Excess weight puts additional stress on the joints, leading to an increased risk of developing arthritis and experiencing joint pain.
- Respiratory issues: High BMI is linked to respiratory problems such as sleep apnea, asthma, and reduced lung function.
- Mental health issues: Individuals with a high BMI may be at a higher risk of developing mental health conditions such as depression and low self-esteem.
What is the formula used to calculate BMI?
The formula used to calculate BMI (Body Mass Index) is BMI = weight (kg) / height^2 (m^2). To calculate your BMI, you need to measure your weight in kilograms and your height in meters. Square your height measurement and then divide your weight by the squared height measurement. The resulting number is your BMI.

For example, if a person weighs 70 kilograms and has a height of 1.75 meters, their BMI would be calculated as follows:
BMI = 70 kg / (1.75 m)^2
= 70 kg / 3.06 m^2
= 22.88
How is BMI used in fitness assessments?
BMI is used in fitness assessments for several reasons. Firstly, it serves as an indicator of overall health, as higher BMI values are associated with an increased risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes.
Secondly, it helps individuals set realistic fitness goals by providing a reference point based on their current weight and desired BMI range. Lastly, tracking changes in BMI over time can help identify trends in an individual’s fitness journey and provide insights into their overall health status.
How is BMI used in weight loss programs?
In weight loss programs, BMI is used as a baseline measurement to track progress and set achievable goals. By regularly monitoring one’s BMI throughout the weight loss journey, it is possible to determine if progress is being made toward reaching a healthy weight.

For example, if an individual’s initial BMI is 30 (considered obese), and their goal is to reach a BMI of 25 (considered overweight), they can set smaller, achievable goals along the way, such as reducing their BMI by 1 point every month. This helps to stay motivated and focused on the weight loss program.
What kind of diets are recommended for maintaining a good BMI?
A balanced and nutritious diet that includes specific food groups can help maintain a good BMI. The recommended diet should consist of approximately 50-60% carbohydrates, 20-30% fats, and 10-20% proteins.
By consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, individuals can ensure they are getting essential nutrients while managing their weight.
How does the DASH diet affect BMI?
The DASH diet has been shown to significantly reduce BMI and contribute to overall weight management. Research indicates that following the DASH diet can lead to an average reduction in BMI of 1.4 kg/m². This eating plan emphasizes the consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products, while minimizing saturated fats, sodium, and added sugars.
What are the criticisms of using BMI?
BMI has several criticisms due to its limitations. These include:
- Fails to differentiate between fat mass and muscle mass, leading to inaccuracies for individuals with high muscle mass, such as athletes.
- Ignores the distribution of body fat, with visceral fat around the organs posing greater health risks than subcutaneous fat.
- Limited applicability across populations, as BMI was originally developed for Caucasian populations and may not accurately reflect body fatness in other ethnic groups.
- Does not consider individual differences, such as age, sex, bone density, and genetic variations, which can influence body composition and health risks.
- Oversimplifies health by not considering other important factors such as fitness level, diet, and lifestyle choices.
What are the limitations of using BMI as a health indicator?
BMI has limitations as a health indicator. It does not differentiate between fat mass and muscle mass, leading to misclassification of individuals with higher muscle mass as overweight or obese, despite having a low percentage of body fat.

Older adults may have a higher BMI due to age-related muscle loss, even if they have a healthy body composition. BMI does not account for differences in bone density, which can vary among individuals.
Additionally, BMI does not consider the distribution of body fat, which is important for assessing health risks associated with excess abdominal fat, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
How accurate is BMI as a measure of body fat percentage?
BMI is not an accurate measure of body fat percentage due to its inability to differentiate between fat mass and muscle mass. It does not account for variations in body composition based on factors such as muscle mass, age, gender, distribution of fat, ethnicity, and overall health.
