Nutrition Facts labels, as defined by Sarah Campos from the University of Waterloo in a 2011 study published in Cambridge University Press, are informational tools found on most packaged foods. They are designed to encourage healthful purchasing and eating habits. In the United States, the usage of these labels has been linked to healthier dietary choices.
Optavia Nutrition Facts refer to the labels on Optavia food products such as shakes, bars, and other Fuelings. These labels provide detailed information about the nutritional content of the product. This includes the list of ingredients, caloric content, amount of dietary fiber, vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients. It also specifies the serving size and any allergen information, as shown in this graph.
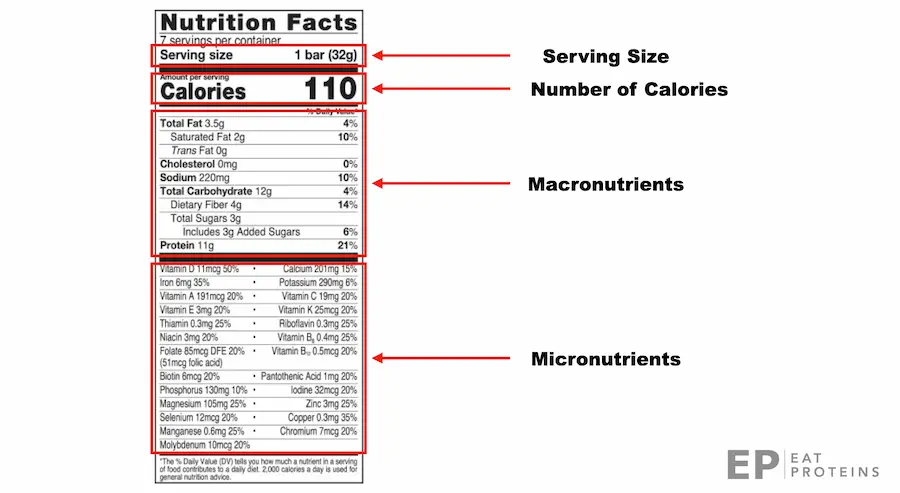
These labels have been a requirement on most packaged foods in the U.S. since the passage of the Nutritional Labeling and Education Act in 1990. In May 2016, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) introduced rules to update the format and content of the Nutrition Facts panel.
Optavia Nutrition Facts aims to inform consumers about what they are consuming, helping them make informed dietary decisions. Questions often surface regarding the Optavia shake nutritional facts, the objective of nutrition labels, and the role ingredient listings play in meal planning.
What ingredients are found in Optavia diet products?
Optavia ingredients as listed in the Optavia nutrition facts refer to the individual components or substances that make up each Optavia diet product or fueling. These ingredients include various types of macronutrients, micronutrients, minerals, and vitamins, as illustrated in this graph.
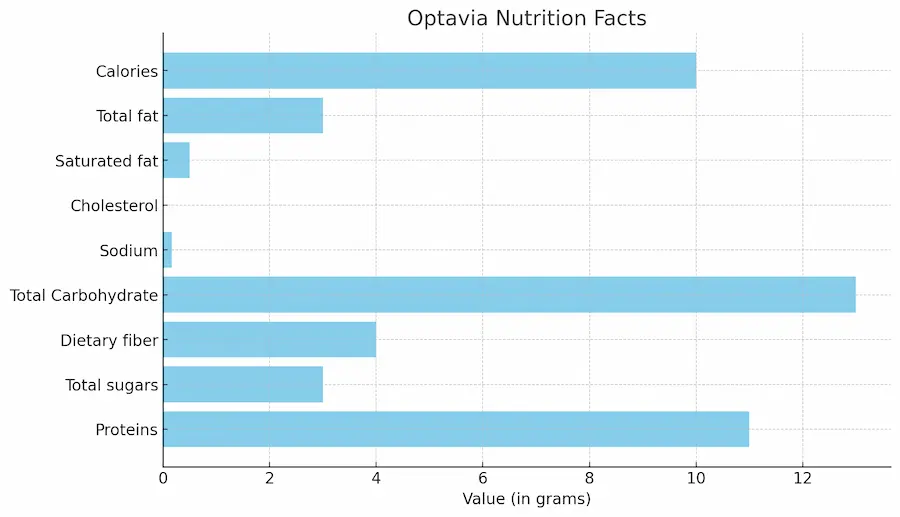
The nine main ingredients found in Optavia Fuelings are listed below.
- Total fat
- Saturated fat
- Trans fat
- Cholesterol
- Sodium
- Total carbohydrate
- Dietary fiber
- Total sugars
- Proteins
1. Total Fat
Total fat refers to the collective amount of all different types of fats, including saturated fats, unsaturated fats, and trans fats, present in a food product or diet. As per the 2021 study by Lukas Schwingshackl, most dietary guidelines recommend that total fat intake should account for 30-35% of total energy intake.
Total fat is a crucial component of a healthy diet, providing energy, supporting cell growth, protecting organs, maintaining body temperature, and aiding in nutrient absorption and hormone production.
The total fat content in Optavia Fuelings varies depending on the specific product, but generally, it ranges from about 1-4 grams per serving.
2. Saturated Fat
Saturated fat refers to a type of dietary fat that is typically solid at room temperature and primarily found in animal products and some plant oils. These fats are fully “saturated” with hydrogen atoms and have no double bonds between the carbon atoms. The saturated fat content in Optavia Fuelings ranges from about 0-2 grams per serving.
Saturated fats play a role in various bodily functions, including the provision of energy, support for cell growth, and aiding in the absorption of certain vitamins. However, excessive intake can increase LDL cholesterol levels, which could potentially contribute to heart disease.
According to the 2018 study by Victoria M Gershuni from the University of Pennsylvania, there is no consistent benefit to all-cause or cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality from reducing dietary saturated fat. This suggests that the amount of saturated fat one should consume may not need to be as strictly limited as previously thought, but it is still generally recommended to limit saturated fat to less than 10% of total caloric intake.
3. Trans Fat
Trans fats, also known as trans-fatty acids, are a type of unsaturated fats that are often created through an industrial process called hydrogenation. These fats are considered harmful for health, particularly when consumed in large amounts.
Trans fats in the diet can have several negative effects: they can distort cell membranes, elevate the risk of coronary heart disease, adversely affect the brain and nervous system, diminish mental performance, and potentially increase the risk of depression, Alzheimer’s disease, and cognitive decline with age.
The 2016 study titled “New data on harmful effects of trans-fatty acids” published in Bratislava Medical Journal suggests that trans fats are unsafe for consumption, leading to a decision by the US FDA in 2015 for complete removal of trans fats from all foods within a three-year time frame. As such, it is recommended that the intake of trans fats should be as low as possible, ideally no more than 1% of total energy intake.
Optavia Fuelings, in line with this recommendation and US FDA regulations, contains 0 grams of trans fat. This aligns with the general guideline to minimize trans fat intake as much as possible for optimal health.
4. Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a type of fat, or lipid, that is produced by the liver and is also present in certain types of foods.
While it is often associated with adverse health effects, cholesterol plays essential roles in the body, including contributing to the structure of cell walls, making up digestive bile acids in the intestine, allowing the body to produce Vitamin D, and enabling the body to make certain hormones.
The cholesterol content in Optavia fuelings varies between 0-5 mg per serving, depending on the type of product.
The effect of dietary cholesterol on health has been the subject of extensive research. Contrary to earlier beliefs, a 2018 study by Ghada A Soliman from The City University of New York showed that there is no substantial evidence to support the notion that dietary cholesterol plays a significant role in developing cardiovascular disease.
However, many foods rich in cholesterol are also high in saturated fats, and it is the saturated fat content that may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
In light of this research, the 2015-2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans removed the previous recommendation of limiting dietary cholesterol to 300 mg per day. However, it’s still advisable to consume cholesterol in moderation, primarily from nutrient-dense sources like eggs and shrimp, which are rich in cholesterol but low in saturated fats.
5. Sodium
Sodium is a mineral that plays an essential role in maintaining proper fluid balance, transmitting nerve impulses, and influencing the contraction and relaxation of muscles. In the diet, sodium mainly comes from salt (sodium chloride).
While sodium is necessary for bodily functions, too much sodium, particularly in the form of dietary salt, can lead to high blood pressure, a risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
On the other hand, a 2020 study by Martin O’Donnell, an Associate Clinical Professor from McMaster University, questions the benefits of a very low sodium diet and suggests that a moderate intake (2.3-4.6g/day; 1-2 teaspoons of salt) may not be associated with increased cardiovascular risk.
Different guidelines suggest different amounts, but a commonly recommended limit is less than 2.3 grams of sodium per day (approximately 1 teaspoon of salt). The American Heart Association recommends an ideal limit of no more than 1.5 grams per day for most adults.
Optavia fuelings are generally lower in sodium compared to other meal replacements. The sodium content in Optavia fuelings typically ranges from about 55-450 mg per serving. This level of sodium contributes to the necessary daily intake while still being mindful of the upper limit.
6. Total Carbohydrate
Total carbohydrates in the diet refer to all the carbohydrates that a person consumes, including sugars, starches, and fibers. Carbohydrates are one of the main types of nutrients and are the body’s primary source of energy.
The effect of carbohydrates on the diet is multifaceted. Carbohydrates provide the body with the energy it needs for physical activity and proper organ function. The brain, in particular, relies on carbohydrates for energy. Some carbohydrates, like dietary fiber, do not provide energy but have other important roles, such as promoting digestive health.
According to the 2021 study by Marleen A. van Baak, there is currently no convincing evidence that manipulating dietary carbohydrates (either reducing the content or changing the type) has a clinically relevant effect on preventing weight regain after weight loss, unless there is an increase in protein intake at the same time.
This highlights the importance of considering the overall composition of the diet, not just a single nutrient.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans suggest that carbohydrates should constitute 45 to 65 percent of your total daily caloric intake. Therefore, if you are following an Optimal Weight 5 and 1 plan (800-1,000 calories per day), between 450 and 650 calories should come from carbohydrates. This equates to approximately 112.5 to 162.5 grams of carbohydrates per day.
The carbohydrate content in Optavia Fuelings typically ranges from about 10-15 grams per serving.
7. Dietary Fiber
Dietary fiber in the diet refers to non-digestible carbohydrates plus lignin. It’s technically a type of carbohydrate, but its non-digestibility (related to its molecular size) distinguishes it.
There are two main types of dietary fiber: soluble, which is found primarily in fruits and vegetables, and insoluble, which is found in cereals and whole-grain products. Most natural, high-fiber foods contain both types.
Dietary fiber has numerous beneficial effects on the diet. It can help maintain bowel health, lower cholesterol levels, control blood sugar levels, aid in achieving a healthy weight, and support overall long-term health.
Soluble fiber can slow the absorption of sugar and improve blood sugar levels, while insoluble fiber can help food move through your digestive system, promoting regularity and helping prevent constipation. The fiber content in Optavia products typically ranges from about 4-5 grams per serving.
According to the 2020 study by Thomas M. Barber from University Hospitals Coventry and Warwickshire, current recommendations for dietary fiber intake for adults in most European countries and the US are between 30-35 g per day for men and between 25-32 g per day for women.
However, it appears that in Europe and the US, actual dietary fiber intake is about one-third below the recommended level. Therefore, most individuals should aim to increase their dietary fiber intake by around 50% compared to their current intake.
8. Total Sugars
Total sugar in the diet refers to all forms of monosaccharides and disaccharides that a person consumes, which provide sweetness and energy. These include both naturally occurring sugars, such as those in fruit and milk, and added sugars, which are added during the processing or preparation of foods and beverages.
According to the 2023 study by Yin Huang, high dietary sugar consumption is generally more harmful than beneficial for health.
Consumption of large amounts of dietary sugar, particularly from sugar-sweetened beverages and added sugars, is associated with various adverse health outcomes, including increased body weight, ectopic fat accumulation, higher risk of gout, coronary heart disease, all-cause mortality, and pancreatic cancer.
Based on the findings of this study, it is recommended to reduce the consumption of free sugars or added sugars to below 25 g/day (approximately 6 teaspoons/day), and limit the consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages to less than one serving per week (approximately 200-355 mL/week) to reduce the adverse effects of sugars on health.
The sugar content in Optavia fuelings typically ranges from about 3-5 grams per serving. This is a relatively low amount of sugar, which helps individuals to stay within the recommended daily limits.
9. Proteins
Protein in the diet refers to a macronutrient composed of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Dietary proteins are essential for numerous bodily functions, including the growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues, the production of enzymes and hormones, and support of the immune system.
According to a 2016 study by Guoyao Wu from Texas A&M University, proteins are hydrolyzed in the digestive tract into amino acids and peptides. These components are either used by bacteria in the small intestine or absorbed into the body’s cells.
Unused amino acids enter the bloodstream for protein synthesis in muscle and other tissues. Amino acids are also used for cell-specific production of low-molecular-weight metabolites with significant physiological importance.
Protein undernutrition can lead to various health issues, such as stunting, anemia, physical weakness, edema, vascular dysfunction, and impaired immunity. The Recommended Dietary Allowance for a healthy adult with minimal physical activity is currently 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. For individuals with minimal, moderate, and intense physical activity, dietary intake of 1.0, 1.3, and 1.6 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day, respectively, is recommended.
The protein content in Optavia fuelings ranges from about 10-15 grams per serving. This can contribute to meeting your daily protein needs while still being consistent with a balanced and moderate approach to protein intake.
What are the Optavia shake nutrition facts?
Optavia shake nutrition facts refer to the detailed breakdown of the nutritional content of Optavia shakes. This includes information on macronutrients like proteins, carbohydrates, and fats (including saturated and trans fats), as well as micronutrients like vitamins and minerals. It also includes information on caloric content, sodium, and dietary fiber.
The purpose of Optavia Shake nutrition facts, as suggested by the 2018 study by Mary J Christoph from the University of Minnesota, is to provide consumers with clear, comprehensive information about what they’re consuming when they drink Optavia shakes.
This information can help individuals make informed decisions about their diet and nutritional intake, potentially assisting in weight management and overall health.
This graph presents the average nutritional facts of seven different Optavia shakes, based on their ingredients.
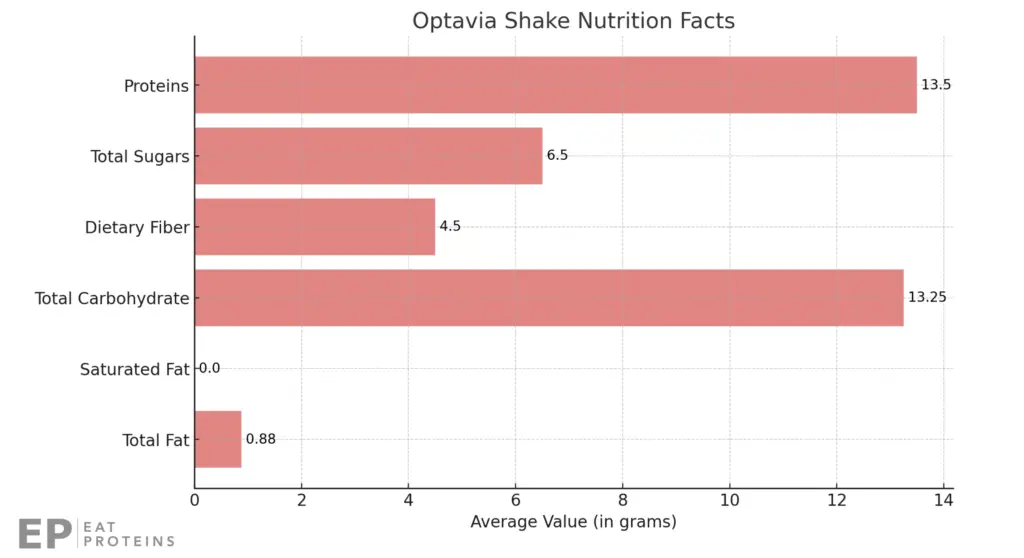
- Calories: 102.5
- Total Fat: 0.875 grams
- Saturated Fat: 0.0 grams
- Cholesterol: 7.5 mg
- Sodium: 237.5 mg
- Total Carbohydrate: 13.25 grams
- Dietary Fiber: 4.5 grams
- Total Sugars: 6.5 grams
- Proteins: 13.5 grams
However, the study also highlights that while nutrition labels can promote healthy behaviors, they can also be associated with unhealthy weight control behaviors, particularly in those at risk for, or engaging in, disordered eating behaviors.
What is the purpose of providing Optavia Nutrition Facts?
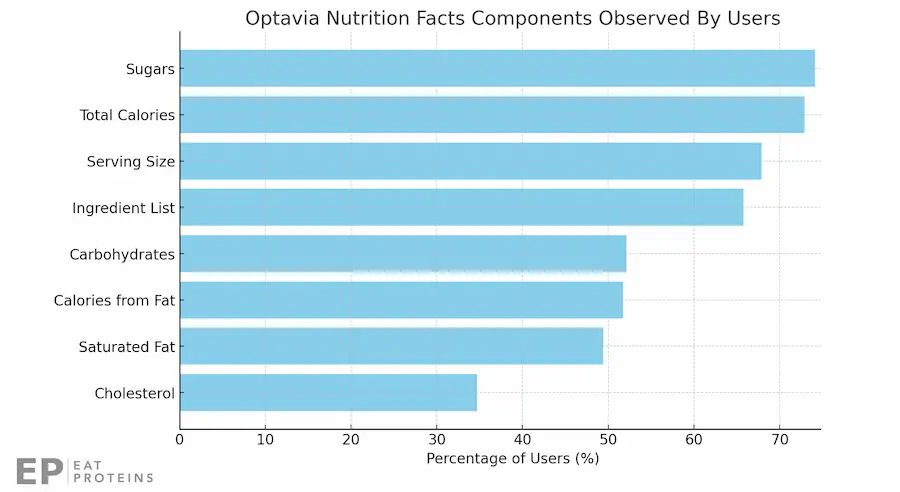
The primary aim of providing Optavia Nutrition Facts is to increase awareness about the nutrient content of the products, as highlighted in a 2018 study published by the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.
According to the study, sugars, total calories, serving size, and the ingredient list are the most frequently observed components of Nutrition Facts, whereas cholesterol is the least observed component, as illustrated in this graph.
How do Optavia Nutrition Facts help people in meal planning?
Optavia Nutrition Facts labels serve as a roadmap for meal planning by detailing key nutritional components like total calories, sugars, and serving size. This empowers individuals to make informed choices, especially when following an Optavia meal plan, whether they’re aiming for weight management or have specific dietary needs.
