The term “GOLO Ingredients” refers to the specific blend of substances used in the formulation of GOLO Release, a supplement capsule designed for weight management and metabolic health. When asked what are the ingredients in GOLO, this blend consists of 7 plant-based ingredients and 3 essential minerals, including chromium, inositol, berberine, and zinc.
According to a 2019 study by Hoda Khorsandi from Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, zinc supplementation has been shown to improve body weight management, inflammatory biomarkers, and insulin resistance in individuals with obesity. In a separate 2020 study by Omid Asbaghi from Lorestan University of Medical Sciences, berberine intake was found to significantly reduce body weight, Body Mass Index, waist circumference, and C-reactive protein levels.
While the ingredients in the GOLO supplement are touted for their antidiabetic properties and ability to improve glycemic responses and aid in weight loss, their effectiveness remains uncertain. This is because the dosages used in scientific studies often exceed the nutritional values present in GOLO Release. Furthermore, as shown in this diagram, the specific quantities of each GOLO ingredient are not disclosed by the company because they are part of a proprietary blend.
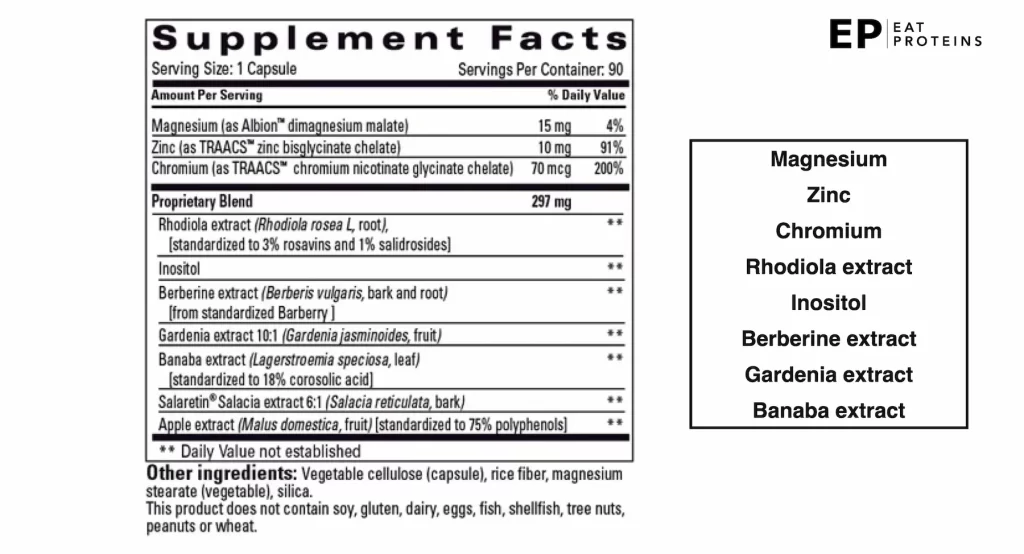
Therefore, the actual efficacy of the supplement is difficult to assess. This article provides a list of 10 GOLO ingredients, which are listed below, highlights their benefits and potential side effects, and offers alternatives.
- Magnesium
- Zinc
- Chromium
- Rhodiola root extract
- Inositol
- Berberine root extract
- Gardenia fruit extract
- Banaba leaf extract
- Salaretin extract
- Apple fruit extract
1. Magnesium
Magnesium, an essential mineral pivotal in over 300 enzymatic reactions, is a key component in the GOLO diet supplement. Each capsule of GOLO Release contains 15 mg of magnesium, amounting to 45 mg per day when taken as recommended.
According to a 2021 study by Mohammadreza Askari from Tehran University of Medical Sciences, taking magnesium in doses ranging from 48 to 450 mg per day for a period of 6 to 24 weeks resulted in a significant decrease in Body Mass Index (BMI). On average, BMI decreased by -0.21 kg/m² across 22 different studies, demonstrating its statistical significance.
This reduction was primarily observed in individuals with magnesium deficiency, insulin resistance-related disorders, and obesity at baseline. No significant changes were seen in body weight, waist circumference, body fat percentage, and waist-to-hip ratio compared to controls.
However, changes in body weight and waist circumference were significant in subgroups with insulin resistance-related disorders, hypertension, obesity, and magnesium deficiency at baseline, as well as in females. The following diagram shows the relation between magnesium dosage and changes in BMI.
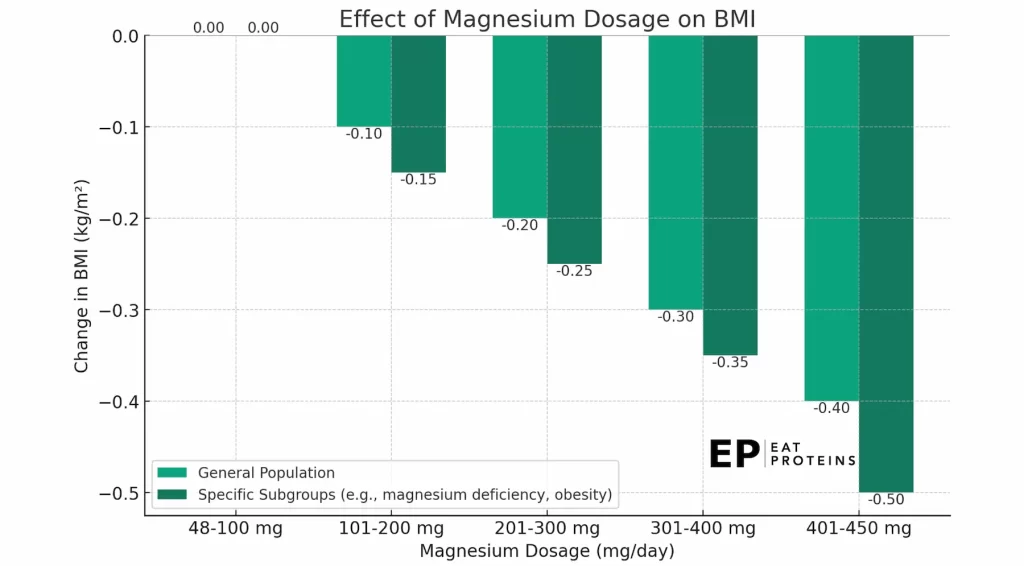
High doses of magnesium, typically above 350 mg per day for adults, can lead to diarrhea and gastrointestinal discomfort. In extreme cases, excessively high levels of magnesium intake (above 5000 mg per day) can result in magnesium toxicity, which may cause symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and even cardiac arrest.
2. Zinc
Zinc is a key component in the GOLO Release supplement, with each capsule containing 10mg, amounting to a daily dosage of 30 mg. This mineral plays a critical role in numerous physiological processes that are vital for health.
According to a 2019 study by Hoda Khorsandi from Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, subjects who received 30 mg/day of zinc supplementation over a period of 15 weeks showed significantly higher reductions in body weight, Body Mass Index, waist circumference, and hip circumference compared to a placebo group. Additionally, the zinc group exhibited lower levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, apelin, and homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR).
The study concluded that zinc supplementation along with a restricted calorie diet has favorable effects in reducing anthropometric measurements, inflammatory markers, insulin resistance, and appetite in individuals with obesity. This scientific evidence supports the rationale behind GOLO’s choice to include 30 mg of zinc per day in its supplement formula.
However, it’s essential to be cautious with zinc supplementation. Consuming more than 40 mg per day can lead to gastrointestinal issues and may interfere with the absorption of other crucial minerals. Extremely high doses, exceeding 200 mg per day, could even lead to zinc toxicity, manifesting symptoms like nausea and loss of appetite. Therefore, adhering to recommended dosages is crucial for maximizing benefits while minimizing risks.
3. Chromium
Chromium is a key ingredient in GOLO Release, with each capsule containing 70 mcg and a daily dosage of 210 mcg. This falls well below the 400 μg per day upper limit mentioned in a 2019 meta-analysis by Catherine Tsang from Edge Hill University. According to Tsang’s research, chromium supplementation can lead to notable reductions in weight, BMI, and body fat percentage, particularly in people who are overweight or obese.
These benefits were most prominent in studies lasting 12 weeks or less and with daily chromium dosages not exceeding 400 μg. While these findings suggest some potential for chromium as a weight-loss aid, the study also cautions that its clinical effectiveness is still uncertain and calls for more research, especially among diabetic patients.
It’s important to note that taking high doses of chromium, specifically over 1,000 μg per day, could lead to adverse effects like stomach issues and low blood sugar, with extreme doses above 5,000 μg per day posing risks of kidney damage and other serious health complications.
4. Rhodiola extract
Rhodiola extract (Rhodiola rosea) is part of the proprietary blend in the GOLO Release supplement, although the exact dosage is not publicly disclosed. The active compounds in Rhodiola rosea, commonly found in Rhodiola extracts, include salidroside and rosavins.
A 2015 study by Elena Pomari from the University of Udine found that Rhodiola rosea extracts have anti-adipogenic and lipolytic activities, particularly in human visceral adipocytes. The study used two extracts containing 3% salidroside or 1% salidroside and 3% rosavins and found significant differences in apoptosis and lipolysis between the treated and control cells. Rhodiola extract also showed a significant decrease in the expression of genes involved in adipocyte function, suggesting its potential role in inhibiting adipogenesis. This research supports Rhodiola’s potential for weight loss and metabolic improvements, although further studies are required for conclusive evidence.
While the study by Elena Pomari did not focus on side effects, it’s generally noted that Rhodiola extract can cause potential side effects like dizziness or dry mouth, especially when taken in high doses exceeding 680 mg per day. Some people may also experience gastrointestinal issues like stomach cramps when taking Rhodiola extract.
5. Inositol
Inositol is included as part of the ingredients in the GOLO Release supplement, although the exact dosage is not specified. It’s a carbohydrate compound often used for insulin-sensitizing purposes.
A 2012 study by Angelo Santamaria from the University of Messina found that myo-inositol treatment significantly improved various metabolic parameters in postmenopausal women affected by metabolic syndrome, except for BMI and waist circumference. The women were given 2 g of myo-inositol twice a day for 12 months, and the results showed improvement in serum glucose, insulin, and lipid profiles.
Another 2012 study by Alessandro D. Genazzani from the University of Modena and Reggio Emilia investigated the efficacy of an 8-week myo-inositol treatment (2 g/day) on insulin sensitivity and hormonal parameters in obese PCOS patients. The study found significant decreases in BMI, insulin resistance, and levels of luteinizing hormone and insulin, particularly in those with high fasting insulin levels.
Generally, inositol is well-tolerated, but high doses exceeding 12 g per day can lead to gastrointestinal issues like nausea, flatulence, or diarrhea. Some individuals may also experience insomnia or dizziness when taking high doses of inositol.
6. Berberine extract
Berberine is a bioactive compound extracted from various plants and is commonly used for its potential benefits in managing metabolic conditions. It has been studied for its effects on obesity, glucose metabolism, and lipid levels. Berberine extract is included in the list of ingredients in the GOLO Release supplement, although its specific dosage is not disclosed.
A 2020 study by Zahra Ilyas from the University of Bahrain reviewed the efficacy of Berberine in managing obesity and related metabolic consequences. In animal models, Berberine was found to affect gut microbiota starting at a dosage of 100 mg/kg/day and inhibit glucose action through α-glycosidase at a dose of 200 mg/kg/day.
Additionally, the compound was effective against the differentiation of adipocytes at 150 mg/kg/day and decreased lipid levels in rats at dosages ranging from 40 mg/kg to 380 mg/kg/day. Human studies confirmed these effects, noting that Berberine could modulate gut microbes at a dose of 500 mg/day and improve glucose accumulation at a daily dose of 1.0 g, as shown in this diagram.
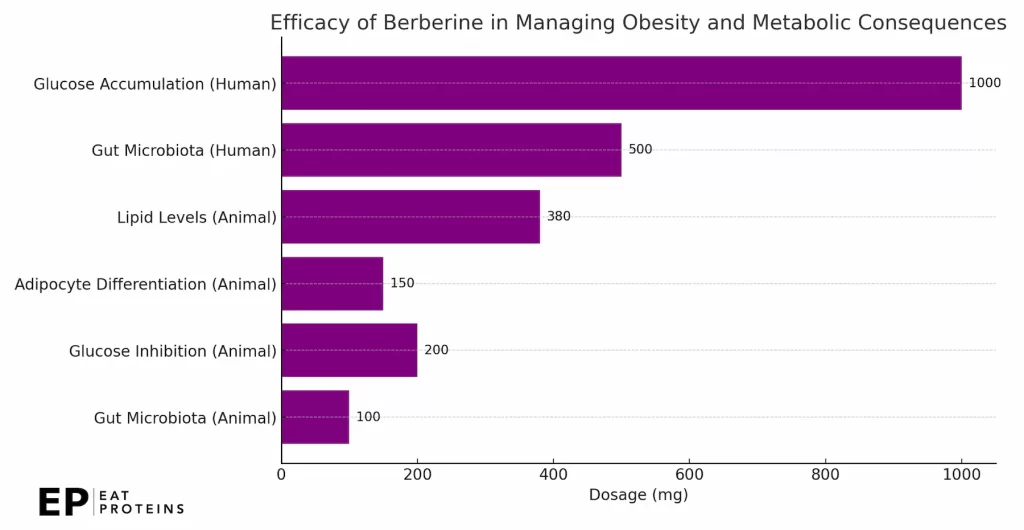
High doses of Berberine, exceeding 2 g per day, can lead to gastrointestinal issues such as cramping, diarrhea, and constipation. Some individuals may also experience low blood pressure when taking Berberine.
7. Gardenia extract
Gardenia extract is derived from the fruit of the Gardenia jasminoides Ellis plant and is known for its potential effects on weight management and energy metabolism. The extract contains various active compounds including Genipin, Geniposide, and Ursolic acid. Gardenia extract is included as part of the proprietary blend in the GOLO Release supplement, but the exact dosage is not disclosed.
According to a 2014 study by Jae Sug Shin from Kyungnam University, Gardenia extract was studied in middle-aged obese women and was found to improve body composition, reduce fat percentage, and positively impact hormones regulating energy metabolism. The study administered 0.08 g per kg of body weight of gardenia extract twice a day for 8 weeks and observed decreases in fat percentage, BMI, and visceral fat area in the participants. The study also found decreased levels of leptin and insulin resistance in the gardenia group compared to the control group. Genipin, one of the key components of gardenia extract, is known to improve insulin resistance and diabetes by ameliorating pancreatic β-cell dysfunction.
While the 2014 study did not focus on side effects, it is generally advised that taking Gardenia extract in high doses can lead to gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea and stomach cramps. There are also concerns about potential interactions with medications, especially those that affect blood clotting.
8. Banaba leaf extract
Banaba leaf extract is derived from the leaves of the Lagerstroemia speciosa L. plant and has been traditionally used in folk medicine to treat diabetes. The hypoglycemic effects of the extract are mainly attributed to its active constituents, corosolic acid, and ellagitannins. Banaba leaf extract is included as part of the proprietary blend in the GOLO Release supplement, but the specific dosage is not known.
According to a 2012 study by Toshihiro Miura from Suzuka University of Medical Science, Banaba leaf extract and its constituent, corosolic acid, can decrease blood sugar levels in human subjects within 60 minutes. Another 1999 study by Ikeda et al. reported a 13.5% average decrease in blood glucose levels in mild type 2 diabetic patients when given a product containing Banaba extract.
A 2006 study published by Tsuchibe et al. revealed a 12% decrease in both fasting and postprandial blood glucose levels after administering 10 mg of corosolic acid daily for 2 weeks. Furthermore, a 2006 study by Fukushima et al. from Kyoto University reported lower blood glucose levels from 60 to 120 minutes in subjects given 10 mg of 99% pure corosolic acid, showing the effects are specifically attributable to corosolic acid.
While most studies have not reported adverse effects with Banaba leaf extract, one report suggested potential nephrotoxicity and lactic acidosis in a diabetic patient with impaired kidney function who was also taking diclofenac. However, the exact role of Banaba or corosolic acid in this case is not clear.
9. Salaretin
Salacia reticulata, commonly known as Kothala Himbutu, is a woody climber plant widely used in Ayurvedic medicine for treating type 2 diabetes and obesity. Its key mechanisms include inhibiting intestinal alpha glucosidase and modulating lipid metabolism. Salacia reticulata is part of the proprietary blend in the GOLO Release pills, but the specific dosage is not publicly disclosed.
According to a 2015 review study by Arjuna B. Medagama from the University of Peradeniya, Salacia reticulata has been shown to inhibit intestinal alpha glucosidase in in-vitro studies. The plant also enhances the mRNA expression for hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) and adiponectin in mouse mesenteric fat, thereby increasing lipolysis and reducing insulin resistance.
Clinical trials indicate clinically significant reductions in HbA1C and plasma insulin levels with treatment durations ranging from 6 weeks to 3 months. One trial also reported a significant reduction in weight and BMI when Salacia is used in combination with vitamin D.
The review did not specifically mention the adverse effects of Salacia reticulata. However, it suggests that a larger evidence base is required to confirm its efficacy and safety, implying that the side effect profile is not yet fully understood.
10. Apple extract
Apple extract (Malus domestica) is derived from apples, one of the most nutrient-rich fruits known for their bioactive compounds including polyphenols, polysaccharides, phytosterols, and pentacyclic triterpenes. These bioactive substances are mainly concentrated in the pulp and peel of the apple and have been studied for their potential health benefits. The proprietary blend of the GOLO Release supplement includes apple extract (Malus domestica), although the precise dosage is not publicly disclosed.
Apple extracts are rich in bioactive compounds that have shown potential health benefits, such as anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. Research indicates that these bioactive substances can contribute to the prevention of cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, inflammation, and cancer. Polyphenols, one of the primary bioactive substances in apple extracts, have been particularly noted for their antioxidant properties. While the exact impact on human health is still under study, these bioactive compounds have been spotlighted as potential regulators against various diseases due to their fewer side effects compared to chemical drugs.
There is limited information on the specific side effects of Apple extract (Malus domestica). However, it is generally considered safe when consumed in moderate amounts, although excessive intake could lead to gastrointestinal issues.
What are the most important ingredients in GOLO?
In the GOLO Release supplement, the most crucial ingredients by dosage are chromium, magnesium, and zinc. These essential minerals are well-known for their roles in various metabolic functions, including the regulation of insulin and glucose metabolism.
While the proprietary blend in GOLO adds an array of other beneficial ingredients, such as Berberine and Inositol, it’s worth noting that its total weight is 279 mg without specific dosage details for individual components. Thus, when considering the importance based on quantity, chromium, magnesium, and zinc stand out as the most significant ingredients in the GOLO supplement.
What are natural substitutes for the ingredients in GOLO for weight loss?
- Ashwagandha
- Cinnamon Extract
- Grape seed extract
- Gymnema Sylvestre
- Fenugreek Seed Extract
- Passionflower Extract
