GOLO diet refers to a weight loss diet that focuses on managing insulin resistance to promote weight loss and improve overall health. The program incorporates a dietary supplement called Release, which is a patented all-natural plant and mineral-based product. On the other hand, the ketogenic (keto) diet refers to a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet designed to shift the body’s metabolism from using carbohydrates to fats as the primary energy source. The diet typically consists of less than 50 grams of carbohydrates per day, with fat intake not being restricted.
When deciding between the Ketogenic diet and the GOLO diet, it’s important to know that the key differences lie in the macronutrient ratios and the use of supplements rather than in how safe or effective they are, as both diets can have varying results. While neither diet is inherently safer or more effective than the other, the Keto diet is generally less expensive and has been more extensively studied in scientific research.
As per definition, the Keto diet is a high-fat, adequate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate eating plan that mimics the metabolism of the fasting state to induce the production of ketone bodies. This fundamental difference in macronutrient ratio and the lack of reliance on supplements largely account for the variations in efficacy, meal planning, cost, and safety between the GOLO and Keto diets. Therefore, choosing between the two is not as straightforward as it might initially appear.
This article delves into the differences between the GOLO and Keto diets, weighing their advantages and disadvantages, and sets them side by side with other weight-loss approaches like the Optimal Weight 5&1 Plan.
What is the Keto Diet?
The ketogenic diet is a dietary approach that involves severely restricting carbohydrate intake between 20 to 50 grams per day while increasing fat consumption. This macronutrient ratio aims to shift the body into a metabolic state called ketosis, where it relies on ketones for energy production. According to a 2020 study by Jennifer T. Batch from Orange Park Medical Center, the ketogenic diet has been associated with advantages such as weight loss, improved insulin sensitivity, and positive effects on cardiovascular risk factors. However, it also has disadvantages including potential side effects and challenges in long-term adherence.
In a 2005 study by William S Yancy, Jr. from Duke University Medical Center, overweight patients with type 2 diabetes following a very low carbohydrate ketogenic diet for 16 weeks saw a significant reduction in their HbA1c levels, decreasing from an average of 7.5% to 6.3%, as shown in this diagram.
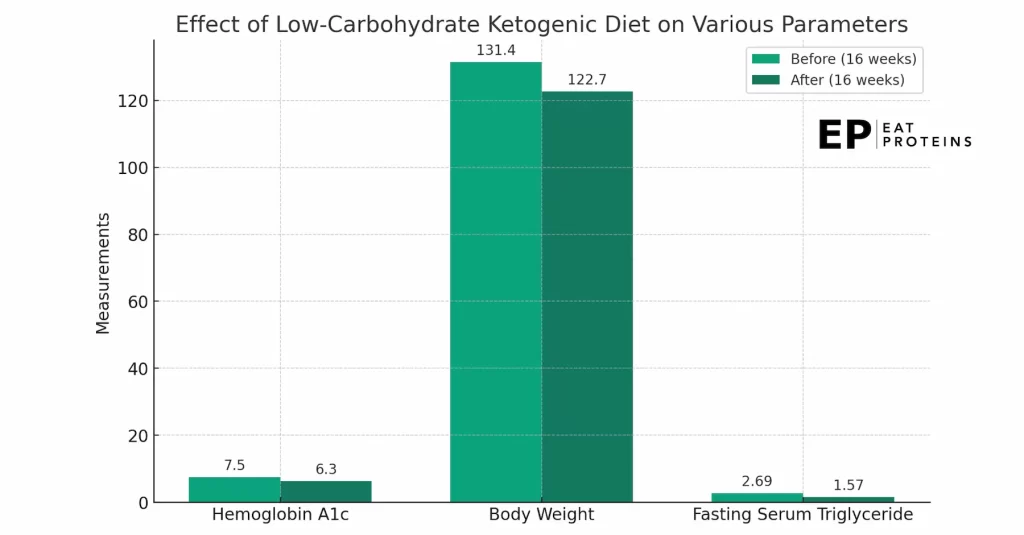
A similar 2018 study from the University of Western Australia on patients with type 1 diabetes found that adherence to a ketogenic diet led to well-controlled Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels of 5.3%, which is considered to be in the normal range according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The fundamental difference between the Ketogenic diet and the GOLO diet lies in the extent of scientific research backing each approach. The Ketogenic diet has been the subject of hundreds of studies, examining its effects on everything from weight loss to metabolic health to neurological diseases. In contrast, the GOLO diet has limited scientific validation, with just one notable study—a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study evaluating its effects, which was funded by GOLO itself.
The main benefit of the ketogenic diet is its proven effectiveness in weight loss and metabolic health, as backed by numerous studies. On average, individuals can experience a weight loss of 5.1-8.7 kg, a decrease in HbA1c levels by 1.0-1.4%, and cardiovascular improvements including a triglyceride reduction of 22.1 mg/dl and an HDL increase of 4.6 mg/dl, according to a 2004 study by Linda Stern from the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center.
The main drawback of the ketogenic diet is that it can increase the risk of heart-related issues by negatively affecting cholesterol levels. Additionally, the diet raises uric acid levels, which can lead to kidney stones. A 2021 study by Dietitian Lee Crosby from the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine also found that the diet can cause digestive problems like constipation and abdominal pain, which can affect long-term adherence to the diet.
What is the GOLO diet?
The GOLO Diet is a weight loss program that aims to optimize your metabolism by balancing insulin levels and reducing Insulin Resistance. It incorporates a patented all-natural plant and mineral-based dietary supplement called “Release,” which is clinically proven to help control insulin, stabilize key hormones affecting weight, and promote fat loss. In a 2019 pilot study by Buynak Clinical Research, people who used the GOLO program lost an average of about 3.3 kg (around 7.3 pounds) in 13 weeks, and their Body Mass Index (BMI) dropped by an average of 1.17, as shown in this diagram.
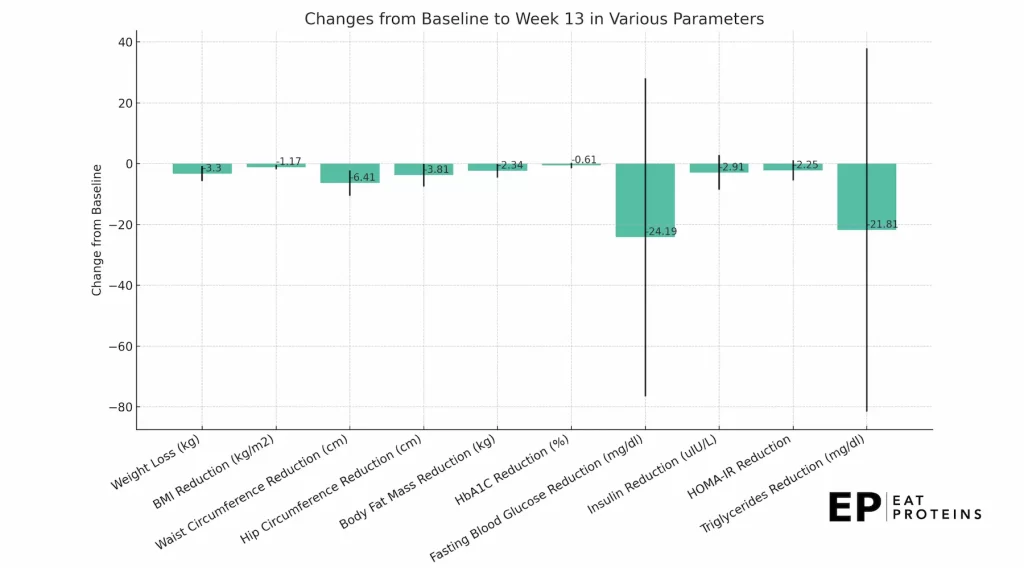
The primary difference between the GOLO diet and the Ketogenic diet lies in their approach to carbohydrates and the physiological state they aim to achieve. The GOLO diet incorporates 20-30 grams of carbohydrates per meal as part of a balanced diet. In contrast, the Ketogenic diet severely restricts carbohydrates, usually to less than 50 grams per day, to induce a state of ketosis where the body burns fat for energy instead of carbohydrates.
The main benefit of the GOLO weight loss diet, as reported in the 2019 pilot study, is significant weight loss and improvement in glycemic control in patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and obesity. The GOLO diet also demonstrated a notable decrease in insulin resistance, with an average reduction in HOMA-IR levels by -35.64%.
The main drawback of the GOLO diet, as presented in the research article, is the high drop-out rate of 40% among the subjects, indicating potential issues with compliance with the diet and exercise components of the program. Additionally, the study was limited by being conducted at only one clinical site, reducing its generalizability.
What are the differences between GOLO and Keto Diet?
The 5 differences between GOLO and Keto are listed below.
- Price differences between Keto and GOLO
- Safety differences between Keto and GOLO
- Meal plan differences between Keto and GOLO
- Availability differences between Keto and GOLO
- Efficacy differences between Keto and GOLO
1. Price differences between Keto and GOLO
The cost of GOLO per month primarily revolves around the GOLO Release supplements, with a single bottle for a one-month supply priced at $59.95. This cost does not include additional expenses like groceries, eating out, or meal delivery. Bulk purchase options can offer some savings, with two bottles available for $99.90 and three bottles for $119.85.
On the other hand, the cost of following a keto diet can vary widely depending on individual choices and needs, but with careful planning, it’s possible to spend between $5 to $10 per day on keto-friendly foods. This amounts to a range of $150 to $300 per month per person. These figures assume you are following budget tips such as buying in-season vegetables, opting for cheaper cuts of meat, and shopping in bulk.
2. Safety differences between Keto and GOLO
The GOLO diet focuses on improving insulin sensitivity and includes a supplement called GOLO Release, which claims to have no known negative side effects. However, the studies supporting these claims are funded by GOLO itself, and as of now, there is insufficient independent peer-reviewed research to definitively verify its safety. If you have diabetes or high blood pressure, it is crucial to consult your doctor before starting the GOLO diet, as the Release pills can affect blood sugar levels and may interact with your medications.
Conversely, while the ketogenic diet has demonstrated short-term advantages like weight loss and lower blood glucose, it also poses questions about its long-term safety. A 2018 pilot study by Wesley C. Kephart from Auburn University revealed a 35% rise in LDL-C (bad cholesterol) among young, fit individuals who followed the diet for 12 weeks. Moreover, a 2017 study by Bernhard Haring from the University of Würzburg linked high animal protein intake, often associated with the diet, to a 23% higher hazard ratio for developing chronic kidney disease over a 23-year period.
3. Meal plan differences between Keto and GOLO
The GOLO meal plan focuses on a balanced, low-glycemic approach to eating, emphasizing whole foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It aims to stabilize blood sugar levels and encourages frequent small meals throughout the day. Carbohydrates are allowed on the GOLO meal plan, but they should be from low-glycemic sources.
On the other hand, the Keto Diet meal plan is high in fats and very low in carbohydrates, aiming to push the body into a state of ketosis where it burns fat for energy. This diet restricts many fruits and vegetables due to their carbohydrate content and heavily emphasizes fats like oils, meats, and dairy. While GOLO has a more balanced macronutrient ratio, keto skews heavily toward fats, with very limited carb intake. This video is from Dr. Mike Varshavski, a family physician from NYC, and it explains what the Keto meal plan is and what to eat.
4. Availability differences between Keto and GOLO
The availability of the Keto and GOLO diets differs significantly in terms of accessibility and distribution channels. GOLO products, such as GOLO Release supplements, are primarily available through their official website or select third-party platforms; however, the comprehensive GOLO Metabolic Plan is exclusively available via the GOLO website. Additionally, GOLO offers a specialized app that provides recipes and meal plans to support users on their diet journey.
On the other hand, the Keto diet is more widely accessible and doesn’t mandate the purchase of specific supplements, although numerous companies do sell keto-friendly products. The Keto diet also benefits from broader commercial support, including specialized restaurants and meal delivery services that cater to its guidelines. This makes the Keto diet more versatile and easier to integrate into various lifestyles compared to GOLO.
5. Efficacy differences between Keto and GOLO
Both the Keto and GOLO diets have demonstrated weight loss results, but the Keto diet has a more robust body of scientific research supporting its efficacy. According to studies, the Keto diet has been shown to be effective in weight loss, improving insulin sensitivity, and other metabolic health markers. In contrast, the GOLO diet has limited scientific validation, primarily backed by one randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study funded by GOLO itself.
With 12.9 million Americans following the Keto diet each year, it has garnered widespread adoption, likely influenced by its well-documented effectiveness. Given that 4 in 10 Americans follow a diet or specific eating pattern, the Keto diet’s popularity and scientific backing make it a more commonly chosen option for weight loss compared to GOLO.
What are the overall pros and cons when comparing GOLO and Keto?
The ketogenic diet offers clear advantages, including substantial weight loss of around 11.2-19.2 pounds on average and improved metabolic health, leading to a reduction in HbA1c levels by 1.0-1.4%. Nevertheless, there are concerns about potential long-term health risks, including raised LDL-C levels and a 23% higher hazard ratio for the development of chronic kidney disease.
On the other hand, the GOLO diet’s main benefit centers around its focus on managing insulin resistance, leading to an average weight loss of approximately 7.3 pounds within 3 months (13 weeks). This approach also brings about a significant decrease in insulin resistance levels. However, it’s important to consider that the GOLO diet incorporates herbal supplements, which might have interactions with medications for some individuals.
What principles do GOLO, Keto, and Optavia diets share?
The GOLO, Keto, and Optavia diets share several principles related to weight loss and health improvement. All three diets emphasize weight loss through different approaches: GOLO focuses on managing insulin resistance, Keto promotes ketosis for fat burning, and Optavia offers rapid weight loss through pre-packaged meals.
Additionally, Optavia and GOLO require either pre-packaged products or supplements to support their respective weight loss strategies.
