The GOLO refers to a commercial weight loss program that combines diet, exercise, and the use of the GOLO Release supplement. The program aims to help overweight or obese individuals achieve gradual weight loss. On the other hand, Ozempic (semaglutide) refers to a drug used for adult patients with type 2 diabetes to improve glycemic control. It can be used as a second-line treatment in combination with metformin or as a third-line treatment with metformin and sulfonylurea.
When choosing between GOLO and Ozempic, it’s crucial to understand two primary distinctions: their mechanisms of action and their classification as either a supplement or a medication. Ozempic is a medication that prompts the body to respond in ways it wouldn’t naturally, such as lowering blood sugar levels, and may require balancing with other medications to mitigate side effects. On the other hand, GOLO is a dietary supplement that comes with a comprehensive meal plan, recipes, and lifestyle changes aiming to provide the body with the tools it needs to naturally improve metabolism and weight.
While a number of studies have shown Ozempic to be associated with a sustained, clinically relevant reduction in body weight, GOLO Release doesn’t require making an appointment with a licensed healthcare professional, as it is available without a subscription and can be purchased from an online store.
The fundamental differences between the two, along with the limited research on the efficacy of weight loss supplements like GOLO, account for most disparities in aspects such as cost, availability, outcomes, and customer reviews. Consequently, the decision between GOLO and Ozempic is not as straightforward as it might initially appear. This article explores how Ozempic and GOLO differ, considers their roles as alternatives in the weight loss market, and examines what sets them apart from other weight loss options.
What is Ozempic?
Ozempic, also known as semaglutide, is a medication primarily used for weight loss and as an adjunct to lifestyle interventions. A 2021 study led by John P. H Wilding from the University of Liverpool showed that adults with obesity taking a 2.4 mg dose of Ozempic once weekly experienced a significant reduction in body weight, averaging a 14.9% decrease over 68 weeks. The medication outperformed the placebo group, where the average weight loss was only 2.4%.
Notably, Ozempic also led to improvements in cardiometabolic risk factors and increased physical functioning according to participant reports. In a 2022 study conducted by Wissam Ghusn from Mayo Clinic, weekly subcutaneous injections of 1.7 mg and 2.4 mg administered over 3 to 6 months led to significant weight loss, mirroring outcomes observed in randomized clinical trials, albeit with less pronounced effects on patients with type 2 diabetes, as shown in this diagram.
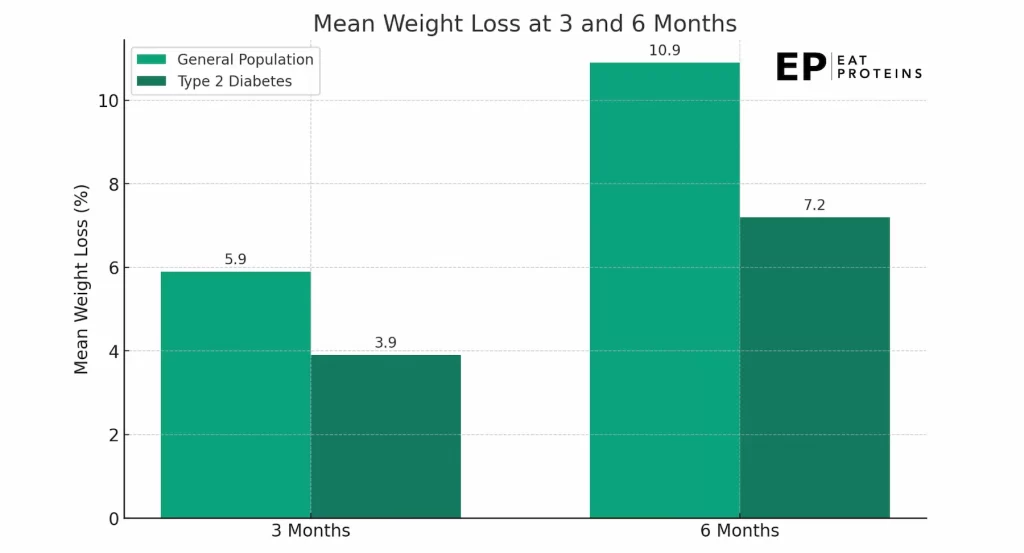
However, the medication can cause side effects such as nausea and diarrhea, and a higher proportion of participants discontinued treatment due to gastrointestinal events compared to those on a placebo.
The primary difference between Ozempic and GOLO lies in the dosage and frequency of intake. Ozempic is typically administered as a weekly subcutaneous injection, with doses ranging from 1700 mcg to 2400 mcg based on clinical research. In contrast, GOLO Release is taken orally three times per day with meals, emphasizing more frequent, smaller doses as part of a dietary supplement regimen.
The main benefit of Ozempic (semaglutide) is its ability to improve glycemic control in adult patients with type 2 diabetes. Clinical studies have shown that once-weekly semaglutide, when used in combination with metformin, can significantly reduce HbA1c levels by up to 1.5%. Additionally, semaglutide has been found to be more effective than sitagliptin in improving glycemic control, with a greater reduction in HbA1c levels of approximately 0.9%.
The main drawback of Ozempic (semaglutide) is its potential side effect of nausea. In clinical trials, approximately 10-20% of patients experienced nausea while taking Ozempic. This adverse effect can be bothersome and may lead to discontinuation of the medication in some individuals.
What is GOLO?
GOLO is a weight loss diet that aims to safely and effectively control sugar cravings, and hunger, and minimize muscle loss while helping individuals reach their goal weight. According to their website, GOLO Diet has over 3 million satisfied customers and a 98% customer satisfaction rating, GOLO has proven clinical results.
In a study conducted by Robert J. Buynak in 2019, participants who were randomly assigned to take the Release supplement showed significant improvements in various body measurements and laboratory tests compared to those who took a placebo. The treatment group experienced a significant weight loss of -6.07 kg, while the placebo group only lost -3.38 kg, as shown in this diagram.
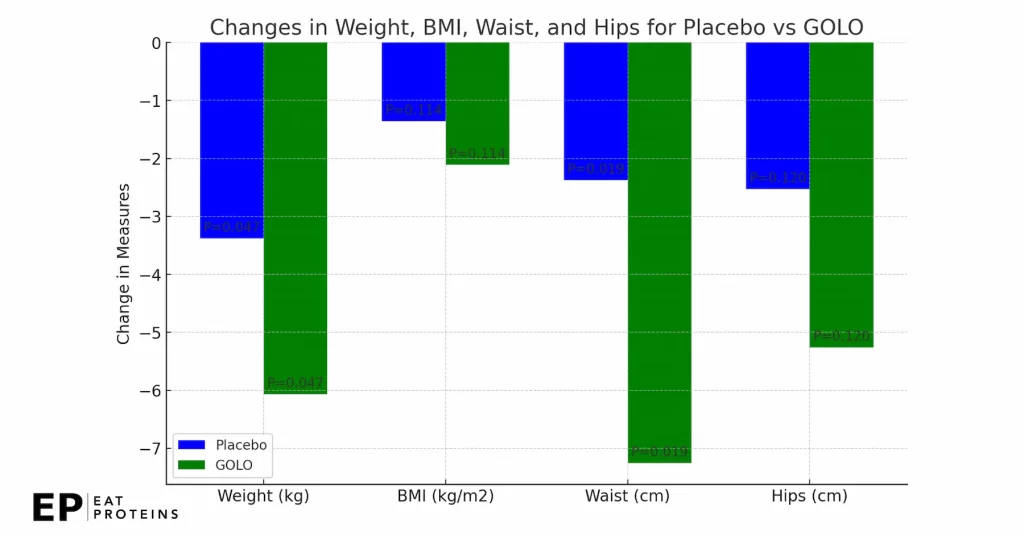
The Release-treated group also saw significant reductions in waist circumference, diastolic blood pressure, and triglyceride levels compared to the placebo group.
The fundamental difference between GOLO and Ozempic lies in their ingredients and mechanisms of action. GOLO primarily relies on chromium supplementation, which has shown some evidence of facilitating minor weight loss, according to a meta-analysis of 11 studies. On the other hand, Ozempic (semaglutide) is a medication that has been studied in clinical trials and is prescribed for more significant weight loss and control of type 2 diabetes, showing weight loss outcomes similar to those in randomized clinical trials.
The main benefit of GOLO is its ability to promote safe and effective weight loss while minimizing muscle loss. According to the GOLO website, customers have reported significant weight loss, with individuals losing an average of 60-202 lbs in a span of 9 months to 13 months.
The main drawback of GOLO is the lack of specific information regarding its effectiveness and safety in terms of long-term weight loss. While testimonials and studies are showing positive results, there is no mention of the average weight loss achieved or the percentage of individuals who maintain their weight loss after using GOLO. Additionally, there are no specific numbers provided regarding potential side effects or any risks associated with using the GOLO program.
What are the differences between Ozempic and GOLO?
The following list shows the 6 primary differences between GOLO and Ozempic.
- Differences in price between GOLO and Ozempic
- Differences in insurance coverage between GOLO and Ozempic
- Differences in scientific research between GOLO and Ozempic
- Differences in efficacy between GOLO and Ozempic
- Differences in availability between GOLO and Ozempic
- Differences in meal plans between GOLO and Ozempic
1. Differences in price between GOLO and Ozempic
When considering the cost of GOLO, it’s worth noting that a single bottle, providing a 30-day supply, is priced at $59.95, resulting in a consistent monthly cost. However, if you opt to purchase 2 bottles together for $99.90, the monthly cost per bottle decreases to $49.95. Furthermore, acquiring 3 bottles for $119.85 offers an even lower monthly cost per bottle at $39.95.
In contrast, Ozempic presents a different pricing scenario. Without insurance coverage, a single injection pen can be quite expensive, with costs typically around $915. Prices may vary between different pharmacies, ranging from $960 to $1,000 per pen. Fortunately, there are options to alleviate these costs, including coupons, prescription cards, and patient assistance programs designed to assist those without insurance in reducing the expense of Ozempic.
2. Differences in insurance coverage between GOLO and Ozempic
GOLO, unlike Ozempic, is not a medication and therefore is not covered by any insurance companies. Ozempic, on the other hand, may be covered by insurance for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and pre-diabetes, though coverage for weight loss purposes can vary.
Insurance plans often have differing coverage policies, leading to a range in the cost of Ozempic with insurance—from as low as $25 per month to full coverage—depending on the specific plan. Healthcare providers have the option to appeal insurance decisions to demonstrate the medical necessity of Ozempic for their patients.
It’s important to note that Ozempic’s insurance coverage has been affected, as some insurance providers and employers are discontinuing coverage for weight loss drugs, including GLP-1s like Ozempic and Wegovy, due to rising costs.
3. Differences in scientific research between GOLO and Ozempic
GOLO has funded a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study that demonstrates the efficacy of their product in weight loss. In contrast, Ozempic, which contains Semaglutide, has a wealth of scientific research dedicated to evaluating its efficacy, dosage, and potential side effects.
This extensive body of research contributes to the comprehensive understanding of Ozempic’s effects. While GOLO’s study provides valuable insights, the sheer volume of scientific research on Ozempic offers a more robust evaluation of its effectiveness and safety.
4. Differences in efficacy between GOLO and Ozempic
Although Ozempic has hundreds of data points backing its weight loss efficacy, including FDA approval for diabetes treatment with weight loss as a side benefit, the situation with GOLO is different. GOLO relies on chromium supplementation, which has shown only modest weight loss effects in randomized clinical trials.
Ozempic, on the other hand, has shown significant weight loss, with some patients losing up to 20% of their body weight. While Ozempic operates as an appetite suppressant affecting gastric emptying, GOLO aims to balance insulin levels, but its clinical relevance in sustained weight loss is uncertain.
5. Differences in availability between GOLO and Ozempic
To get Ozempic, a prescription from a licensed healthcare professional is essential, which can be acquired through in-person consultations with a doctor or via online platforms that provide virtual medical evaluations. It’s crucial to consult with a trusted healthcare professional to determine the most suitable method for obtaining Ozempic.
In contrast, GOLO can be easily purchased directly from the GOLO website, and it doesn’t necessitate any pre-assessment, prescription, or consultation with a healthcare provider. This straightforward accessibility sets GOLO apart as a convenient option for those seeking a weight management solution.
6. Differences in meal plans between GOLO and Ozempic
GOLO provides a comprehensive meal plan that utilizes a point-based system, allowing users to choose from over 30 categories of healthy recipes. Users following the GOLO meal plan typically have weekly guidelines that allocate a certain number of points for different food categories, encouraging a balanced diet.
In contrast, Ozempic does not offer a meal plan, focusing instead on the medication’s physiological effects for weight loss. Ozempic patients have weekly visits with a doctor to monitor the medication’s efficacy and side effects but receive no nutritional guidance as part of the treatment.
What are the overall Pros and Cons when comparing Ozempic and GOLO?
One major pro of Ozempic is its clinically proven effectiveness in controlling blood sugar levels and aiding in weight loss, backed by extensive scientific research and FDA approval. GOLO, on the other hand, offers a holistic approach to weight management by including a comprehensive meal plan and recipes, making it easier for users to incorporate lifestyle changes.
A drawback of Ozempic is that it can come with a range of side effects, such as gastrointestinal issues, and requires regular medical monitoring, which may not be convenient for all users. GOLO’s disadvantage lies in its lesser degree of clinical validation when compared to Ozempic, as its efficacy is primarily supported by user testimonials rather than rigorous scientific studies.
What are the alternatives to Ozempic and GOLO?
This list shows the alternatives to Ozempic and GOLO.
- Rybelsus
- Trulicity
- Mounjaro
- Metformin
- Wegovy
- Saxenda
- Bydureon
- Victoza
- Plenity
What are the alternative diets to Ozempic and GOLO?
The alternative diets to Ozempic and GOLO are shown below.
- Weight Watchers
- Wonderslim
- Ketogenic diet
- Optavia
- NOOM
- Nutrisystem
- Jenny Craig
How do Ozempic and GOLO compare to the Keto diet?
Ozempic is a medically prescribed drug primarily for diabetes control that also aids in weight loss by suppressing appetite; it doesn’t prescribe a specific diet but is often used in conjunction with a doctor-recommended eating plan, which may or may not align with the high-fat, low-carb principles of the Keto diet.
GOLO focuses on a comprehensive meal plan and recipes designed to balance insulin levels, which is a different approach from the Keto diet that aims to put the body into a state of ketosis for weight loss.
While both GOLO and the Keto diet offer structured eating plans, the differences between GOLO and Keto lie in their nutritional philosophies; GOLO emphasizes a balanced diet that includes carbohydrates, whereas the Keto diet severely restricts carb intake to achieve ketosis.
How do Ozempic and GOLO compare to the Plenity?
While Ozempic is an injectable medication primarily used for managing type 2 diabetes and aiding in weight loss, both GOLO and Plenity offer alternative approaches to weight management, with GOLO providing an herbal supplement alongside a meal plan, and Plenity available as a prescription-only oral hydrogel.
